Entering ItemType Properties
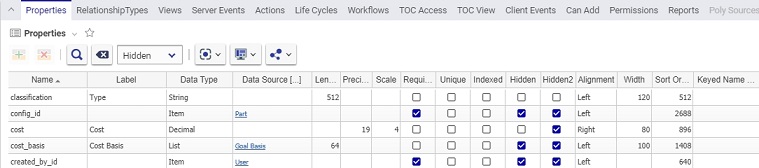
The Properties tab in ItemTypes contains all the properties of the item, including system properties. Click on the Properties tab in the ItemType form. You should see something like the following:
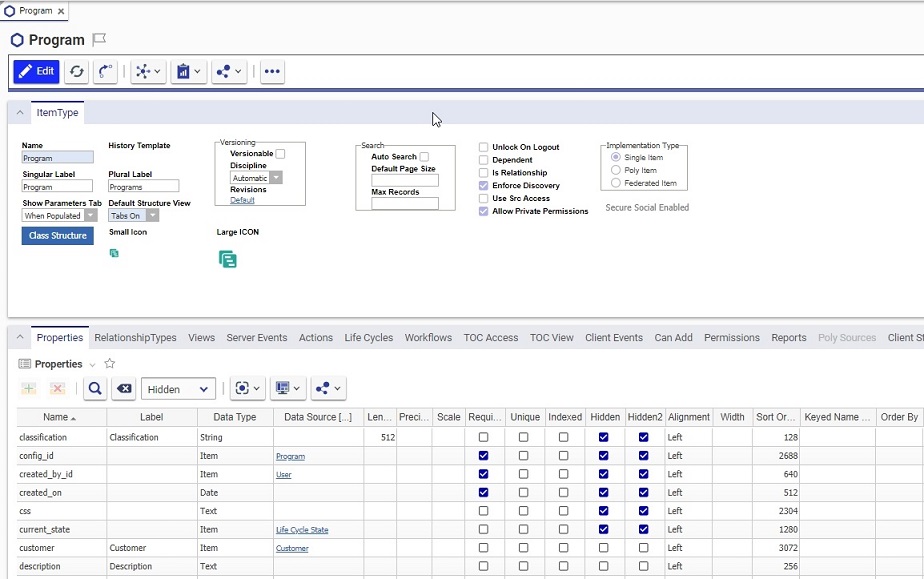
When you create a new property, a new line in the properties grid is created, which then needs to be populated by user values.
Creating a property
-
Open the ItemType and click
 . The ItemType is claimed by you which means no one else can edit it.
. The ItemType is claimed by you which means no one else can edit it. -
Click on the Properties tab.
-
Click the Add Row icon
 . A new row is added at the bottom of the grid.
. A new row is added at the bottom of the grid. -
Enter the values for each column as required. For an explanation of what each column specifies, see the following table.
|
Column |
Description |
|
Name |
Unique, internal name of the property |
|
Label |
The name label for the property displayed on item forms and grids |
|
Data Type |
Determines the data type of the property - such as String, List, etc. |
|
Data Source |
If the property data type is a List, a Sequence, an Item or some other data type that requires a source of information to receive its data, then the data source is specified here. The type of data source depends on the data type. |
|
Length |
The maximum number of characters for String data type. |
|
Precision |
For properties of Data Type = “Decimal”, Precision sets the total number of digits both left and right of the decimal point. For example, for a Decimal property A precision is set to 5, valid values for A could be: 12345, 12.345, 1234.5, etc. |
|
Scale |
Sets the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the Data Type = ”Decimal”. For example, for a Decimal property A whose precision is set to 5, and scale is set to 2, valid value would be: 123.45, 12.45, 12.40 |
|
Required |
Boolean. When checked, it means that the value of the property cannot be null. For properties of Data Type Text, there is currently a special work around for setting and resetting the value of Required. |
|
Unique |
If true, the property value must be unique among all item instances of this ItemType |
|
Indexed |
If true, it means that the database tables will be indexed on this property in order to increase the performance of frequent searches on this particular property. |
|
Federated |
The value for this property will be provided from outside Innovator by a custom Method. The data should match the property Data Type for setting and displaying. |
|
Hidden |
If true, this property will not be displayed in any of the property grids for the items. For example, one of these grids is displayed when the ItemType is selected from the TOC.
Above you can see the properties which are not hidden. The rest, such as the system properties, do not appear on the grid |
|
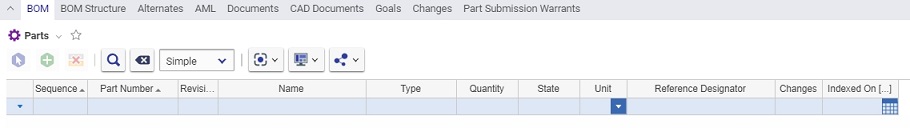
Hidden2 |
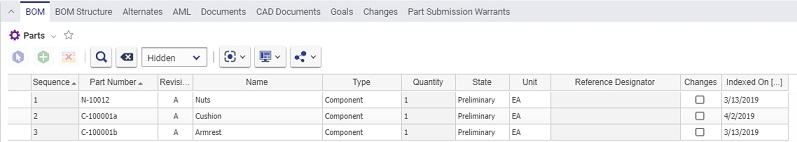
If true, this property will not appear on the relationship grid. For example, look at the Part ItemType. Notice that the only properties which are NOT set to true for Hidden2 (put a 0 in the search criteria of Hidden2 and search) are:
When the Part instance is created, and the BOM Tab is exposed, notice that it is only these properties (plus some BOM relationship properties, such as Sequence, Quantity, and Reference Designator) which are visible:
|
|
Alignment |
Determines the alignment of the values within the grid cell. Possible values are Left, Right, or Center. Left is the default. |
|
Width |
Determines the width of the column in the property grids (in pixels). In the example below, the Length was set to 30, while the rest are 100.
|
|
Sort Order |
Integer values control the relative position of columns in the search grid display with lower values left to right. For example, the GeometricShape properties Classification, Color, and Radius are set as follows: 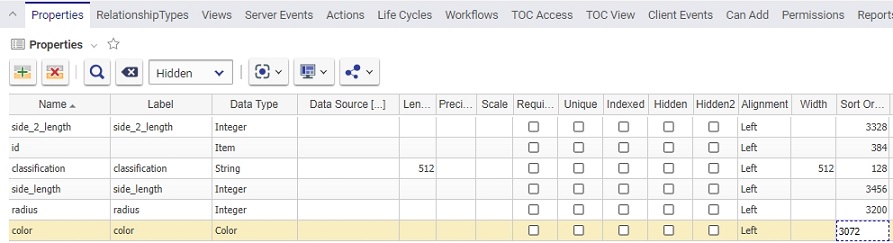
which results in the main item grid displayed as:
|
|
Keyed Name Order |
The keyed name is the name that will be used in system messages to refer to the Item, usually the label or name of the item. If no keyed name for an ItemType is specified, a unique, internal name will be used. You may concatenate as many property values as necessary to identify the item in a meaningful way. The properties used in the Keyed Name must have an order number assigned to them. For example, say you have an item Employee with properties Firstname and Lastname. Keyed Name Order value of 1 in the Firstname field and 2 in the Lastname field would generate a keyed name in the form “John Jones”. |
|
Order By |
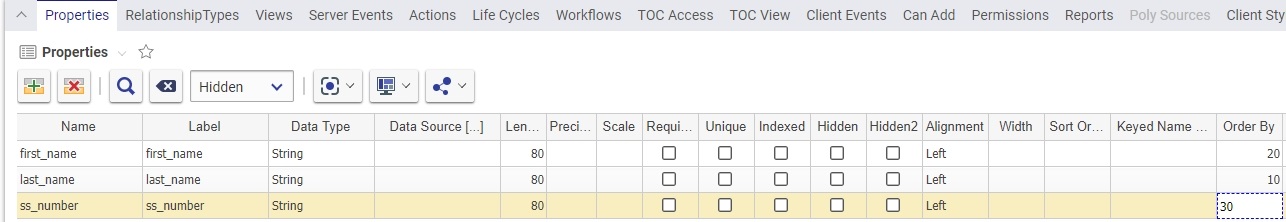
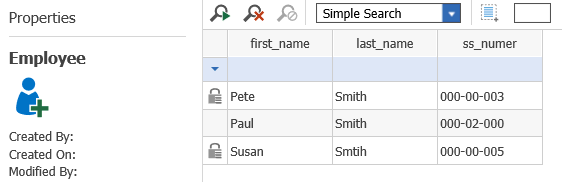
Controls the order (top to bottom) of the items displayed in the main item grid, either after a manual or an automatic search. Whichever property has the lowest value of Order by, is the first one to control the order. For example, if you want to order the employees by last name and then by first name, Lastname would have a value of 1 in the Order By property, and Firstname would have a value of 2. Here is an example of an ItemType called Employees, notice that each property has a value for Order By.
Here is an example of several employees sorted according to the attribute set above:
Notice that the Last Name is first criteria, then, within the all the members of the same last name, Innovator orders by the first name (Order By = 20). Then, within the members of the same last name and first name, Innovator orders by SS Number. |
|
Default Value |
The default value of a property to be used if no value is given. Blank represents a Null value. Sometimes, it's a good idea to have a default value for the required properties. |
|
Default Search |
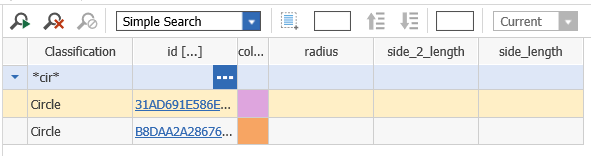
When the user goes to the main item page, they usually perform a search, or a search is automatically performed for them (if the Auto Search property is checked). The value of Default Search property is entered as a search criteria, displayed in the blue line above the grid. So, for example, if in the GeometricShape, we enter *cir* in the Default Search column of the Name property, then, when the main GeometricShape page is accessed and the search is performed, the result is as shown below. Notice that the Default Search value appears in the blue line of the specified property.
|
|
Pattern |
This applies only to properties of type String, or Filtered List. In prior releases Pattern was used to format properties of type Date, but formatting of dates is now part of Internationalization and Localization. If the property is of type String, then the pattern will follow the basic regular expression syntax. These patterns are used for data validation on the server side, and should be used for fields such as a phone number, an e-mail address, or perhaps a social security number. For example, for a phone number, you could use the following pattern: \d{3}-\d{3}-\d{4}. If the property if of type Filtered List, then Pattern is the pointer to a property which defines the filter. For more information, please see Filtered List. |
|
Foreign Property |
This field basically echoes a property value of a property defined for a different Item. It is required that another property, say property A, of type Item is defined. Then, the Foreign Property, can reference any property of the item defined by property A. This field is also populated automatically when the ItemType definition is saved. For example, say you wanted to create an ItemType definition for a Part. You want to associate the engineering specification with each instance of Part. So, for the Part ItemType definition, you create a property, called Specification Document which is of type Item, and whose Data Source would be Document. Then, you can create another property, called Spec ID, of type Foreign, whose Data Source would point to the Name property of Document. Once you save the ItemType definition for Part, you should see name appear in the Foreign Property field. For more examples and definitions of how this works, see Foreign Data Type. |
|
Item Behavior |
For properties where the data type = Item, and the target item specified by the property is versionable; Item Behavior specifies Fixed or Float. Fixed means that this property points to a specific generation of target item, even if newer ones are created. Float means that this property points to the latest generation of the target item. |
|
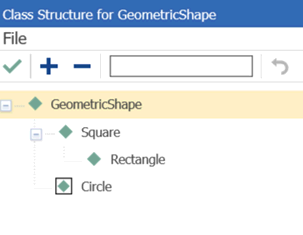
Class Path |
If the Item has a class structure, you can specify which subclass this property belongs to. All subclasses below the chosen subclass will inherit this property as well. If no subclass is specified, then it is assumed that the property belongs to the parent ItemType. For more information refer to Class Structure. To insert the class path for the property, simply click in this cell. The class structure dialog (shown below) is displayed. Select the subclass node to which this property belongs. Click the green check
|
|
Tooltip |
|
|
Help Text |
|
|
Track History |
|

 to complete your selection.
to complete your selection.